Common AWS Elastic Beanstalk Docker issues and solutions.
ArticleIn this article I will be writing about common issues that I’ve stumble upon using AWS Elastic Beanstalk running Docker environment. I will be updating this article in future each time I stumble upon new issue (…or remember old one) that may happen to you.
Pull Requests are welcome to add more know-hows to this article (Github logo at the bottom will redirect you to git source of this Markdown file) as well as any unanswered question and Feedback in comment section bellow.
Debugging Tools and files
Docker stats
In order to debug Docker memory / CPU consumption of given Docker container you can do:
# Get docker container ID
sudo docker ps
# CONTAINER ID
# 8eff1959c23c
# stats on it
docker stats 8eff1959c23c
CONTAINER CPU % MEM USAGE/LIMIT MEM % NET I/O
8eff1959c23c 0.02% 44.16 MiB/300 MiB 14.72% 278.5 MiB/62.68 MiB
Read more https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/stats/
Overal Docker stats / info
docker info will give you several usefull information:
sudo docker info
# Containers: 4
# Images: 180
# Storage Driver: devicemapper
# Pool Name: docker-202:1-143330-pool
# Pool Blocksize: 65.54 kB
# Backing Filesystem: extfs
# Data file: /dev/loop0
# Metadata file: /dev/loop1
# Data Space Used: 4.493 GB
# Data Space Total: 107.4 GB
# Data Space Available: 45.69 GB
# Metadata Space Used: 8.86 MB
# Metadata Space Total: 2.147 GB
# Metadata Space Available: 2.139 GB
# Udev Sync Supported: true
# Data loop file: /var/lib/docker/devicemapper/devicemapper/data
# Metadata loop file: /var/lib/docker/devicemapper/devicemapper/metadata
# Library Version: 1.02.89-RHEL6 (2014-09-01)
# Execution Driver: native-0.2
# Kernel Version: 3.14.48-33.39.amzn1.x86_64
# Operating System: Amazon Linux AMI 2015.03
# CPUs: 1
# Total Memory: 3.665 GiB
# Name: ip-172-31-31-219
# ID: MJVD:KSNK:3VLH:JYXK:HRXT:UVA2:JKLZ:FFK7:HXYL:7ZEU:DCHZ:JT2R
read more https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/info/
eb console
AWS Elastic Beanstalk provides EB CLI
$ eb from which you can do lot of debugging operations. All you need
is to cd to the directory where you hold Dockerrun.aws.json file and
lunch it from there
cd ~/folder_where_I_hold_Dockerrunjson/
eb deploy
# will `tar` the dir and deploy it to AWS EB = it will deploy your app
eb status
# Environment details for: myApplication
# # ....
# Status: Ready # when `Updating` it means that either deployment running or some env config is beeing updated you need to wait while finishes
# Health: Green # when `Red` it means that either load balancer cannot access it or the instance is down. Sometimes it happens when CPU is to high
eb events -f
# events that are currently happening on that server e.g.:
# Deploying new version to instance(s). - deployment in progress
# Batch 3: Starting application deployment on instance(s) [i-fe87ae73] - what instance is beeing update
eb ssh
# ssh to the instance.
note:
eb sshwill work only if you have private key that is allowed to access to server is your~/.ssh/dir and you specify the name of that ssh key infolder_with_dockerrun_json/.elasticbeanstalk/config.ymlindefault_ec2_keyname. Look at articles Appending Example 1
Important log files
ssh to AWS instance (eb ssh)
/var/app/current/Dockerrun.aws.json- view currently deployed EB configuration file/var/log/eb-activity.log- log files of AWS events such as steps that are done in order to downloading credentials, pull Docker images, as well as hook methods./var/log/dockerand/var/log/docker-events- what is happening with docker images aftereb-activityfinishes - e.g. starting containers, die, …
Restarting a server
AWS ElasticBeanstalk VMs are configured in a way that it should be ok to restart them at any point. (all configuration is remembered unless your DevOps guy is done some custom changes)
eb ssh
# once in
sudo shutdown -r now
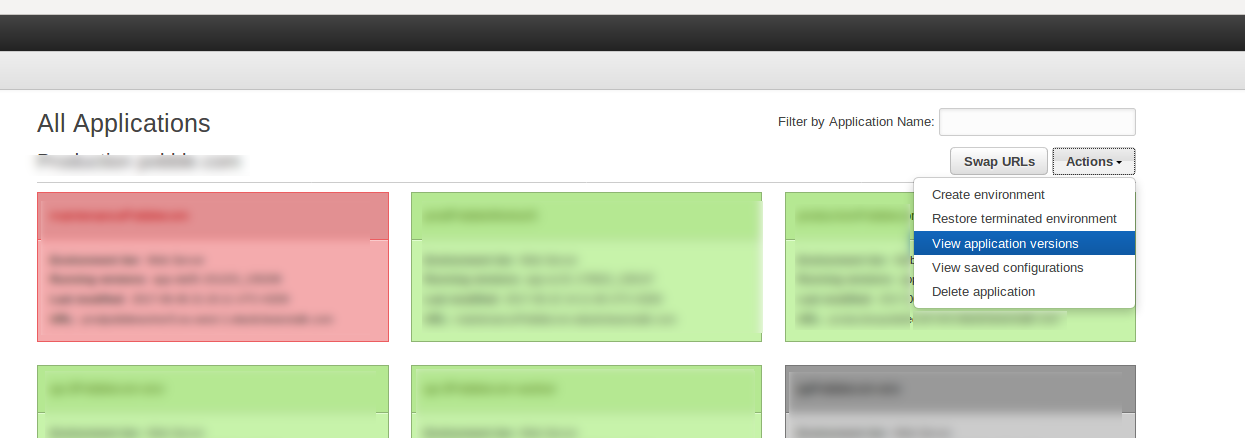
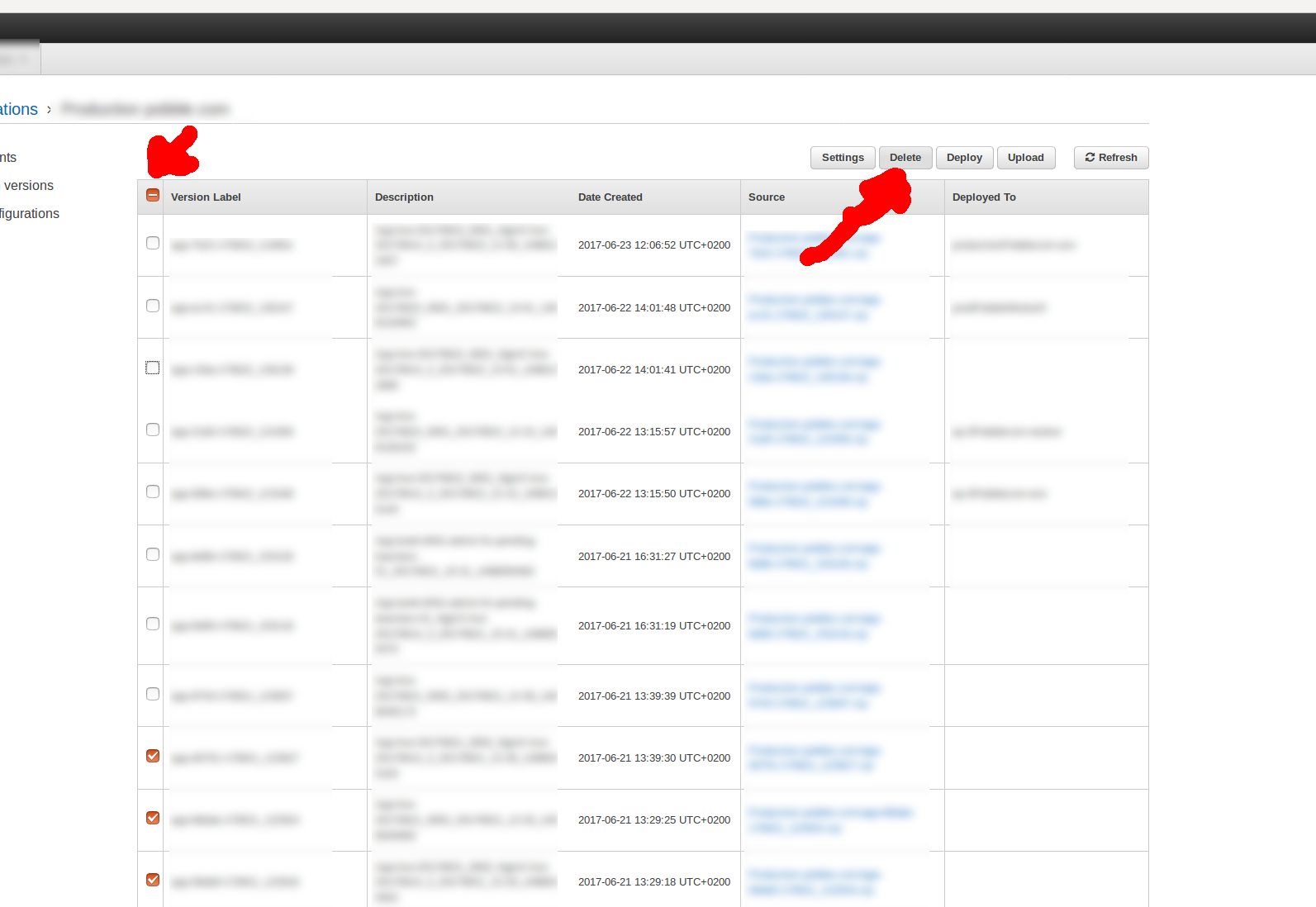
500 Application Versions limit reached
if you get error:
ERROR: You cannot have more than 500 Application Versions. Either remove some Application Versions or request a limit increase.
you need to remove old Application versions. To do that go to enviroment application versions and select all versions and unselect some of the latest versions that are active (you need to have those versions presents in case Load Balancer introduce new instances -> that application version zip file will be called)
Application log files
I recommend to read this article as it fully explain how you can aggregate logs from your containers
The bottom point is that AWS EB is aggregating logs to host VM
/var/log/containers/containername
So if your container name is "name": "nginx-proxy" then it will be /var/log/containers/nginx-proxy. That being said, this only works if you set standard EB
log mount point matching awseb-logs-containername:
{
"AWSEBDockerrunVersion": 2,
"containerDefinitions": [
{
"name": "nginx-proxy",
"image": "nginx",
# ...
"mountPoints": [
# ...
{
"sourceVolume": "awseb-logs-nginx-proxy",
"containerPath": "/var/log/nginx"
}
]
}
]
}
Like I said read the mountPoints section of EB documentation if you want full details.
The point is that this way EB will collect container logs so that they are “accessible” with eb logs download feature
Note: EB is already aggregating your Docker containers STDIO to
/var/log/containers/
Load balancer issues
When setting up new ElasticBeanstalk or when cloning Elastic beanstalk enviroment, AWS will copy the LoadBalancer setup. But this clonning is not perfect. Some time lot of security groups are not imported and sometimes new ones are introduced that may be totaly paranoid
This happened to me recently while cloning EB enviroment. Clone loadbalancer had new security group that had Outband rule only for HTTP but not HTTPs. Due to this loadbalancer was saying no instances are healthy even though they were responding to healthcheck.
Given admin ssh to instance (eb ssh)
When curl loadbalancer healthcheck endpoint localhost/heacheck
Then I get 200 response
But Given I curl curl loadbalancer healthcheck endpoint on Elastic beanstalk dns endpoint my-app.elasticbeanstalk.com/heacheck
Then I have no response
So solution was to check not only Inbound rules of EC2 security groups but also Outbound rules of AWS Elastic Loadbalancer
EC2 instance cannot pull docker image from ECR
You are able to configure your docker container to be AWS ECR as descirbed here
It use to work out of the box before but since 2019 docker on EB EC2 instance require docker login
To do it for each deployemnt you need to provide Elasticbeanstalk deployment hook
cat .ebextensions/91_login_to_aws_ecr.config
commands:
20_login_to_aws_ecr_before_pull:
command: sudo $(sudo aws ecr get-login --no-include-email )
Common server issues when docker is not starting
Let say for no good reason (or after deployment) docker containers seems to start and die
tail -f -n 333 /var/log/docker-events.log
# something like :
# 2016-05-12T00:50:48.000000000Zddbde24a9b7dbf5156f1e74cd0d5f0e7463e49f3435c5b9423a5fba0969f3735: (fromequivalent/my_docker_app) start
# 2016-05-12T00:50:49.000000000Zddbde24a9b7dbf5156f1e74cd0d5f0e7463e49f3435c5b9423a5fba0969f3735: (fromequivalent/my_docker_app) die
# 2016-05-12T00:51:48.000000000Zddbde24a9b7dbf5156f1e74cd0d5f0e7463e49f3435c5b9423a5fba0969f3735: (fromequivalent/my_docker_app) start
# 2016-05-12T00:51:49.000000000Zddbde24a9b7dbf5156f1e74cd0d5f0e7463e49f3435c5b9423a5fba0969f3735: (fromequivalent/my_docker_app) die
Server run out of space
check space usage
df -h
# Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
# /dev/xvda1 30G 24G 25G 99% /
# devtmpfs 2.0G 112K 2.0G 1% /dev
# tmpfs 2.0G 0 2.0G 0% /dev/shm
check particular folder
sudo du -sh /var/log
# 49G /var/log
docker images may be takeing too much space
sudo du -sh /var/lib/docker/
13G/var/lib/docker/
sudo du -sh /var/
sudo docker rmi -f $(sudo docker images | grep "<none>" | awk "{print\$3}") # Get rid of all untagged images.
I’m recommending to check http://www.eq8.eu/blogs/23-spring-cleaning-for-webdevelopers
Image doesn’t exist
First just check cat /var/app/current/Dockerrun.aws.json and if the
image specified in it is the one you want.
In 90% cases the docker would be
failing just because you mistyped image name (e.g.
"image":"quay.io/myorg/myapp:live_20160101,",)
If the tail -n 333 -f /var/log/eb-activity.log is saying something
like “Docker image not found” or “You don’t have permissions to access
this image” it’s usually due this:
- misspelled docker image / endpoint (e.g.
"image":"quay.io/myorg/myapp:live_20160101,", - wrong credential file name in the
Dockerrun.aws.json(look at Appending Example 2) - credentials inside the bucket are not correct (look at Appending Example 3)
Out of memory
let say that /var/log/docker-events have something like
2016-05-12T00:51:01.000000000Z4edd70df83997cdd5487a684b7a1ae2021072627efa7d1db909bb4270d36fbf4: (fromequivalent/little_bastard:latest) start
2016-05-12T03:31:42.000000000Zedcdaf5426465b92519df0b81a3706d0033c329cd2d7aaddf5c4bb7f2ee9752e: (fromequivalent/little_bastard:latest) oom # <<< !!!! important
2016-05-12T03:31:42.000000000Zedcdaf5426465b92519df0b81a3706d0033c329cd2d7aaddf5c4bb7f2ee9752e: (fromequivalent/little_bastard:latest) die
…the oom means that docker image equivalent/little_bastard don’t
have enough memory allocated
Solution: in the ElasticBeanstalk application environment
Dockerrun.aws.json
"containerDefinitions": [
{
"name": "request_repeater",
"image": "equivalent/little-bastard",
"essential": true,
"memory": 80,
…increase the memory allocation (`“memory”: 80 to e.g. “memory: 100)
Appendix
Example 1 .elasticbeanstalk/config.yml
branch-defaults:
default:
environment: name-of-my-enviroment-qa
production
environment: name-of-my-enviroment-production
global:
application_name: Production myapp.com
default_ec2_keyname: myapsecretkey
default_platform: Multi-container Docker 1.6.2 (Generic)
default_region: us-east-1
profile: eb-cli
sc: null
Example 2 - authentication in Dockerrun.aws.json
# ...
"authentication": {
"bucket": "myapp.com.systems",
"key": "dockercfg"
},
# ...
Example 3 - corrent credentials inside bucket file
if you use quay.io
{
"auths": {
"quay.io": {
"auth":"ZxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxT0=",
"email": "[email protected]"
}
}
}
if you use dockerhub
{
"auths": {
"https://index.docker.io/v1/": {
"auth": "Zxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxq",
"email": "[email protected]"
},
}
}
Entire blog website and all the articles can be forked from this Github Repo